Cryptocurrency trends are reshaping the financial landscape, offering both opportunities and challenges. From market fluctuations to technological advancements, the cryptocurrency space is constantly evolving, attracting institutional adoption and revolutionizing various sectors.
As the cryptocurrency industry matures, it is crucial to stay abreast of the latest trends to make informed decisions and navigate the evolving landscape effectively.
Market Overview: Cryptocurrency Trends

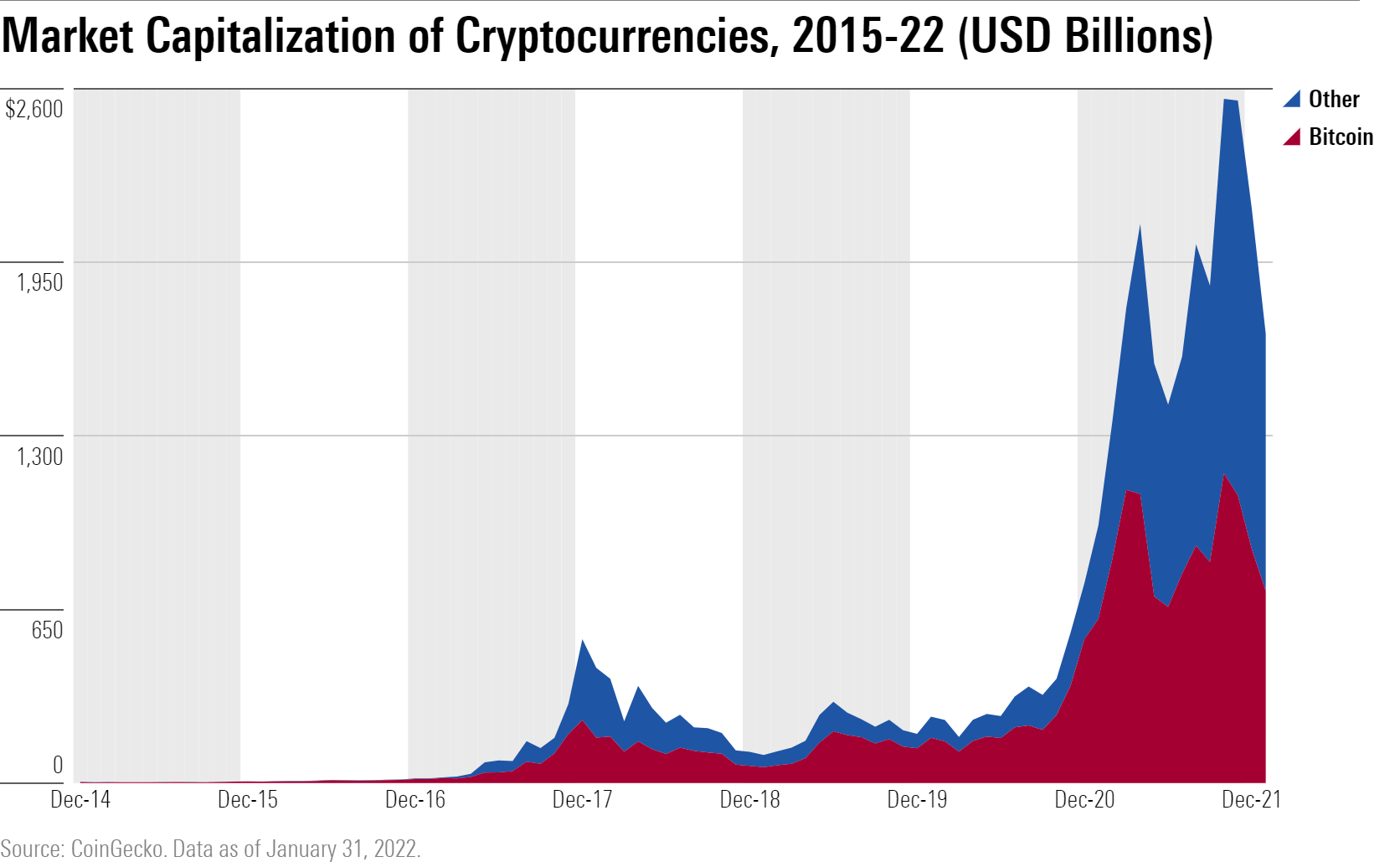
The cryptocurrency market has witnessed a remarkable expansion in recent years, with its total market capitalization surpassing the trillion-dollar mark. The surge in trading volume has also been substantial, indicating a growing interest in digital assets.
Historically, the cryptocurrency market has experienced significant fluctuations, with periods of rapid growth followed by sharp corrections. These fluctuations have been driven by a combination of factors, including regulatory changes, technological advancements, and global economic conditions.
Key Factors Influencing Market Performance, Cryptocurrency trends
The performance of the cryptocurrency market is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Institutional Adoption:The increasing involvement of institutional investors, such as hedge funds and pension funds, has brought legitimacy and stability to the market.
- Regulatory Landscape:Government regulations and policies have a significant impact on the cryptocurrency industry, shaping its legal framework and operating environment.
- Technological Innovations:Advancements in blockchain technology, such as the development of decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs), have expanded the use cases for cryptocurrencies.
- Economic Conditions:Macroeconomic factors, such as inflation, interest rates, and global economic growth, can affect the demand for cryptocurrencies as an alternative investment or store of value.
- Media Sentiment:Positive or negative media coverage can influence public perception and drive market sentiment, impacting cryptocurrency prices.
Technological Advancements
The cryptocurrency space is constantly evolving, with new technological advancements emerging all the time. These advancements are having a major impact on the industry’s growth and adoption. Here are some of the latest developments:
Blockchain technologyis the foundation of all cryptocurrencies. It is a distributed ledger system that allows for secure, transparent, and tamper-proof transactions. Blockchain technology is constantly being improved, with new features and applications being developed all the time.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts that are stored on a blockchain. They can be used to automate a wide variety of tasks, such as transferring funds, executing trades, and managing supply chains. Smart contracts are still in their early stages of development, but they have the potential to revolutionize many industries.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi is a new financial system that is built on blockchain technology. DeFi applications allow users to borrow, lend, trade, and invest in cryptocurrencies without the need for a traditional financial institution. DeFi is still in its early stages of development, but it has the potential to make financial services more accessible and affordable for everyone.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
NFTs are unique digital assets that are stored on a blockchain. They can be used to represent ownership of anything from digital art to real estate. NFTs are still in their early stages of development, but they have the potential to create new markets and opportunities for creators and collectors.
These are just a few of the latest technological advancements in the cryptocurrency space. These advancements are having a major impact on the industry’s growth and adoption. As these technologies continue to develop, we can expect to see even more innovation and disruption in the years to come.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape for cryptocurrencies is evolving rapidly, as governments around the world grapple with how to regulate this new asset class. In some jurisdictions, such as the United States and the European Union, cryptocurrencies are considered to be commodities and are regulated accordingly.
In other jurisdictions, such as China and South Korea, cryptocurrencies are considered to be securities and are regulated as such.The potential impact of government regulations on the cryptocurrency industry is significant. Regulations could make it more difficult for cryptocurrency businesses to operate, and could also deter investors from participating in the market.
However, regulations could also provide clarity and certainty for the industry, and could help to protect investors from fraud and abuse.The key regulatory challenges facing the cryptocurrency market include:
- Anti-money laundering and counter-terrorism financing (AML/CTF):Cryptocurrencies can be used to launder money and finance terrorism, and regulators are concerned about the potential for these activities to increase as the cryptocurrency market grows.
- Consumer protection:Investors in cryptocurrencies are not always aware of the risks involved, and regulators are concerned about the potential for them to lose money.
- Market manipulation:The cryptocurrency market is still relatively small and unregulated, and this makes it susceptible to manipulation. Regulators are concerned about the potential for market manipulation to harm investors and undermine the integrity of the market.
The cryptocurrency industry is working with regulators to address these challenges and develop a regulatory framework that will protect investors and promote innovation. However, it is likely that the regulatory landscape for cryptocurrencies will continue to evolve for some time.
Institutional Adoption

Institutional adoption of cryptocurrencies has been growing in recent years, as more and more traditional financial institutions recognize the potential of digital assets. This trend is being driven by a number of factors, including the increasing maturity of the cryptocurrency market, the development of new and more sophisticated cryptocurrency products and services, and the growing regulatory clarity around cryptocurrencies.Institutional investors are attracted to cryptocurrencies for a number of reasons.
First, cryptocurrencies offer the potential for high returns. Second, cryptocurrencies are a new and innovative asset class that can help to diversify an investment portfolio. Third, cryptocurrencies are increasingly being seen as a store of value, similar to gold.The growing institutional adoption of cryptocurrencies is having a number of implications for the market.
First, it is helping to legitimize cryptocurrencies and make them more attractive to a wider range of investors. Second, it is increasing the demand for cryptocurrencies, which is driving up prices. Third, it is helping to develop new and more sophisticated cryptocurrency products and services.
Examples of Institutional Investors Who Have Invested in Cryptocurrencies
* Grayscale Investments:A digital asset management firm that offers a variety of cryptocurrency investment products.
Fidelity Investments
A global financial services firm that offers a cryptocurrency custody service.
BlackRock
The world’s largest asset manager, which has recently announced plans to offer cryptocurrency investment products.
Security and Fraud
Cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology are not immune to security risks. The decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies makes them vulnerable to hacking and fraud. Exchanges and wallets have been hacked, resulting in the theft of millions of dollars worth of cryptocurrency.
Mitigating Security Risks
To mitigate these risks, several measures are being taken:
Stronger encryption
Cryptocurrencies use strong encryption algorithms to protect transactions and data.
Two-factor authentication
Many exchanges and wallets require users to enable two-factor authentication (2FA) to add an extra layer of security.
Smart contracts
Smart contracts can be used to automate transactions and enforce rules, reducing the risk of fraud.
Regulation
Governments are working on regulating cryptocurrencies, which could help to improve security and reduce fraud.
Security Breaches
Despite these measures, security breaches have occurred. In 2014, Mt. Gox, one of the largest Bitcoin exchanges at the time, was hacked, resulting in the theft of 850,000 Bitcoins. In 2016, The DAO, a decentralized autonomous organization, was hacked, resulting in the theft of $50 million worth of Ether.These breaches have had a significant impact on the market, causing investors to lose confidence and prices to fall.
However, the industry has learned from these breaches and is taking steps to improve security.
Use Cases and Applications

Cryptocurrencies have found applications in various sectors, offering unique benefits and challenges. Their decentralized nature, immutability, and anonymity make them suitable for diverse use cases.
From digital payments to decentralized finance, cryptocurrencies are transforming industries and creating new opportunities.
Digital Payments
- Fast and low-cost transactions:Cryptocurrencies facilitate instant and cost-effective payments globally, bypassing traditional banking systems and high fees.
- Cross-border transactions:They eliminate currency conversion fees and delays, making international payments more accessible and efficient.
- Access to financial services:Cryptocurrencies provide financial inclusion to individuals in regions with limited access to traditional banking services.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
- Peer-to-peer lending and borrowing:Cryptocurrencies enable decentralized lending and borrowing platforms, offering competitive interest rates and flexible terms.
- Automated market making:Cryptocurrencies facilitate automated market makers (AMMs), which provide liquidity and enable trading without the need for intermediaries.
- Yield farming:Users can earn passive income by lending or staking their cryptocurrencies in liquidity pools or decentralized applications.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
- Digital art and collectibles:NFTs are used to represent ownership and authenticity of unique digital assets, such as art, music, and videos.
- Virtual real estate:Cryptocurrencies are used to purchase and trade virtual land in online worlds, creating new investment opportunities.
- Event ticketing:NFTs can be used as tickets for events, offering secure and tamper-proof verification.
Supply Chain Management
- Transparency and traceability:Cryptocurrencies enable the tracking of goods and materials throughout the supply chain, ensuring transparency and preventing fraud.
- Efficient payments:Cryptocurrencies facilitate instant and secure payments between suppliers and manufacturers, reducing delays and costs.
- Smart contracts:Automated contracts based on blockchain technology can trigger actions based on specific conditions, such as product delivery or payment.
Final Thoughts
The cryptocurrency market is poised for continued growth and innovation, with advancements in technology, regulatory frameworks, and use cases shaping its future. As institutional adoption increases, the mainstream acceptance of cryptocurrencies will likely accelerate, further transforming the financial ecosystem.
Understanding and embracing these trends is essential for businesses, investors, and individuals seeking to capitalize on the opportunities and mitigate the risks associated with cryptocurrencies.
Questions Often Asked
What are the key factors driving cryptocurrency market fluctuations?
Market sentiment, regulatory developments, technological advancements, and macroeconomic conditions are among the key factors influencing cryptocurrency price movements.
How is blockchain technology revolutionizing industries?
Blockchain provides transparency, security, and efficiency, making it applicable in supply chain management, healthcare, voting systems, and many other fields.
What are the regulatory challenges facing the cryptocurrency industry?
Regulatory frameworks for cryptocurrencies vary across jurisdictions, creating uncertainty and hindering wider adoption. Governments are working to establish clear guidelines to balance innovation with investor protection.
